Host TurboPlayer Service in a Windows Service - Single configuration
Requirements
Run PowerShell as an Administrator
Since v2.0.74.0, the majority of TurboPlayerService API’s require the TurboPlayerServiceLicense.dll be present
Prepare the Environment (If Necessary)
Download the complete TurboPlayerService software package
IMPORTANT: at the moment, the TurboPlayerService.deps.json, TurboPlayerService.runtimeconfig.json and runtimes/ should exist in the package in order to have it successfully running
Install .NET 6 Runtime and .NET 6 Core Runtime
Visit https://dotnet.microsoft.com/en-us/download/dotnet/6.0
Download the “..NET 6 Runtime” Hosting Bundle and install it.
Download the “.NET 6 Core Runtime” and install it.
Create service configuration in the Parameters Service
Create service configuration with all necessary parameters as described here DigaSystem registry subkeys and parameters
Create configuration files
Create file AppSettings.json
This file is the standard configuration file for .NET 6 Core applications and is mandatory to start the service. See more information here Service configuration file - Single configuration, how to create & configure it
Hint. By the first installation rename the file template_AppSettings.json to AppSettings.json This file contains all parameters required for service configuration and requires only to fill with the real values (e.g. URLs for the DPE services)
Hint. Don’t forget to fill configuration name created in the Parameters Service as a configuration name in AppSettings.json
Create file log4net.json
This file contains configuration for the file log and strongly recommended being configured. Service can use this log if DPE Log Service isn’t available or logged information is too big. See more information here Logging, how to create & configure it
Hint. By the first installation rename the file template_log4net.config to log4net.config This file contains a typical configuration for file log and can be used without changes in mostly standard workflows even with multiple service configurations workflows or can be used as a start point to optimize file log for custom workflows.
Create the Windows Service
Create Windows service
To create the Windows Service, use the native Windows Service Control Manager's (sc.exe) create command.
sc.exe create "$TurboPlayerServiceInstanceNameOfYourChoice" binpath="C:\Path\To\TurboPlayerService.exe"
# OUTPUT: [SC] CreateService SUCCESSCheck the result
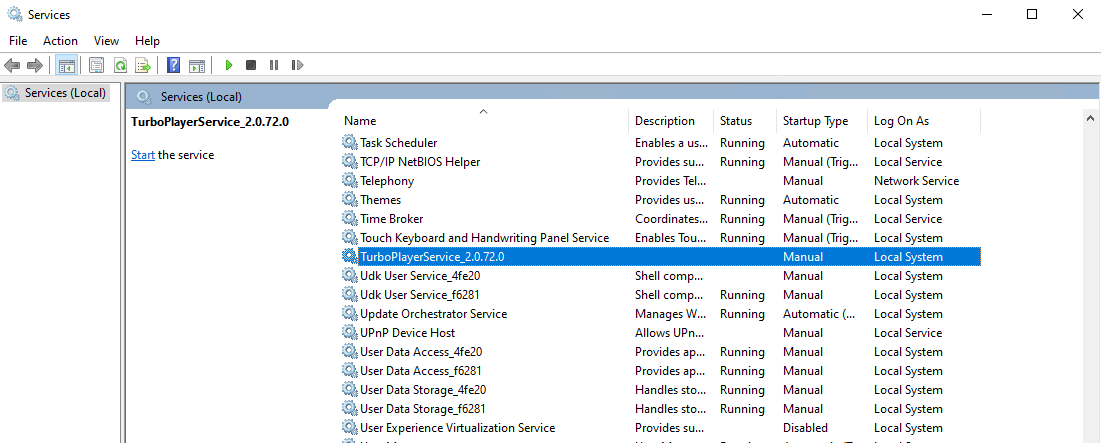
After successfully creating the service, you can find it in the Windows Services, such as the following.
Configure the Windows Service
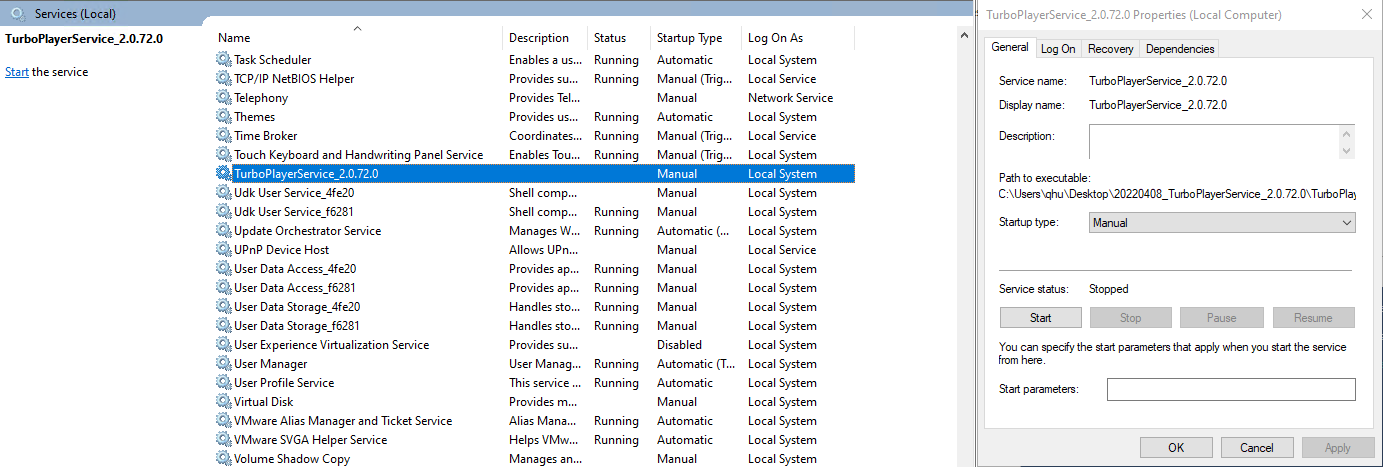
The service can be configured like all other typical Windows services via context menu and dialogs.
Start and Stop the Windows Service
When you followed the configuration steps, the service can be started and stopped like all other typical Windows services. (As a general reminder, a complete configuration would typically include an appsettings.json configuration files (like for all other .NET 6 applications; TurboPlayerService release contains a template_appsettings.json for reference) and correctly configured DigaSystem registry parameters (which is unique to TurboPlayerService as specified in the aforementioned configuration page.).)
Define the URLs to use
This part is not specific to TurboPlayer Service hosted in a Windows Service. It is also valid when TurboPlayer Service is hosted by other containers, such as a PowerShell environment. However, it makes sense to keep it here to ease the installation of TurboPlayer Service hosted in a Windows Service.
By default, the TurboPlayer Service like all other standard .NET 6 Core web applications will listen on port 5000 if no URL and port definition given.
In general, there are several ways to define the Urls for a .NET 6 Core web applications. However, in the context of an application hosted in a Windows Service, there is just one recommended way, as given in the following.
The recommended way is to define Urls in the appsettings.json file or in the DigaSystem registry under the subkey "TurboPlayerService". The easiest way is to do it in the appsettings.json file.
The Urls follows the standard pattern supported by all standard .NET 6 Core web applications. (The value provided can be one or more HTTP and HTTPS endpoints (HTTPS only if a default cert is available). Configure the value as a semicolon-separated list (for example, "Urls": "http://localhost:8000;http://localhost:8001").)
For only HTTP, it is recommended to use the "Urls" in appsettings.json:
{
"Urls": "http://*:11250"
}For both HTTP and HTTPS, it is recommended to use "Kestrel" in appsettings.json:
{
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"Http": {
"Url": "http://*:11250"
},
"HttpsInlineCertFile": {
"Url": "https://$FQDN:11251",
"Certificate": {
"Path": "C:\\Path\\To\\ValidCertificate.pfx",
"Password": "$Password"
}
}
}
}
}N.B. The HTTPS URL will not work automatically without making the following HTTPS configuration. In fact, it will stop TurboPlayer Service from successfully starting.
There are many more different ways to configure HTTP URLs and HTTPS URLs. For the biggest possibility, please reference the documentation given by Microsoft at https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/fundamentals/servers/kestrel/endpoints?view=aspnetcore-6.0.
(Worth mentioning, according to some comments on the Internet, when the key "Kestrel" is configured, the key "Urls" may not take effects.)
Verify the running TurboPlayer Service instance
TurboPlayerService API to check WebSocket requests
{{service_host_name_or_ip}}/turbo/ws
Delete the Windows Service
To delete the Windows Service, use the native Windows Service Control Manager's (sc.exe) delete command.
sc.exe delete "$TurboPlayerServiceInstanceNameOfYourChoice"
# OUTPUT: [SC] DeleteService SUCCESSTroubleshooting
Windows could not start the service on Local Computer
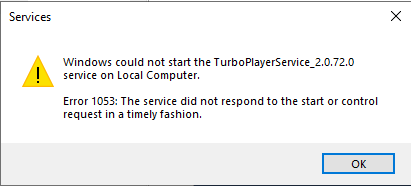
There could be many causes which lead to this issue.
The first diagnose method is to start the TurboPlayerService as a CLI program and check the output.
The second diagnose method is to check the log file (for example, Log/TurboPlayerService.log) for possibly useful information.
In Windows PowerShell: The required library hostfxr.dll could not be found.
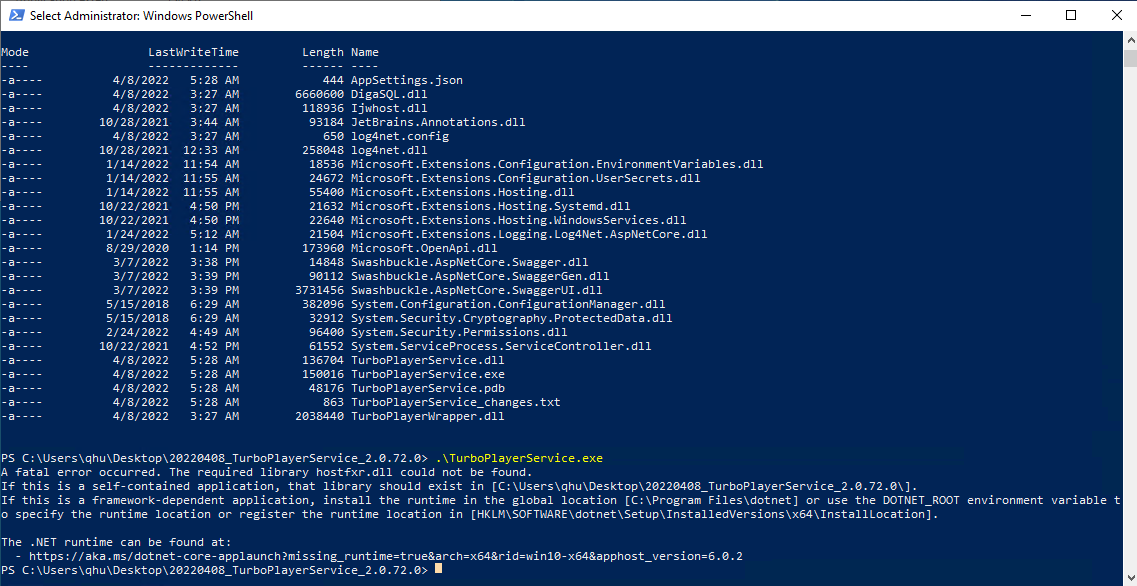
It could be the .NET 6 runtime is not installed, please try to install the .NET 6 runtime environment as given in the "Prepare the Environment" section.
